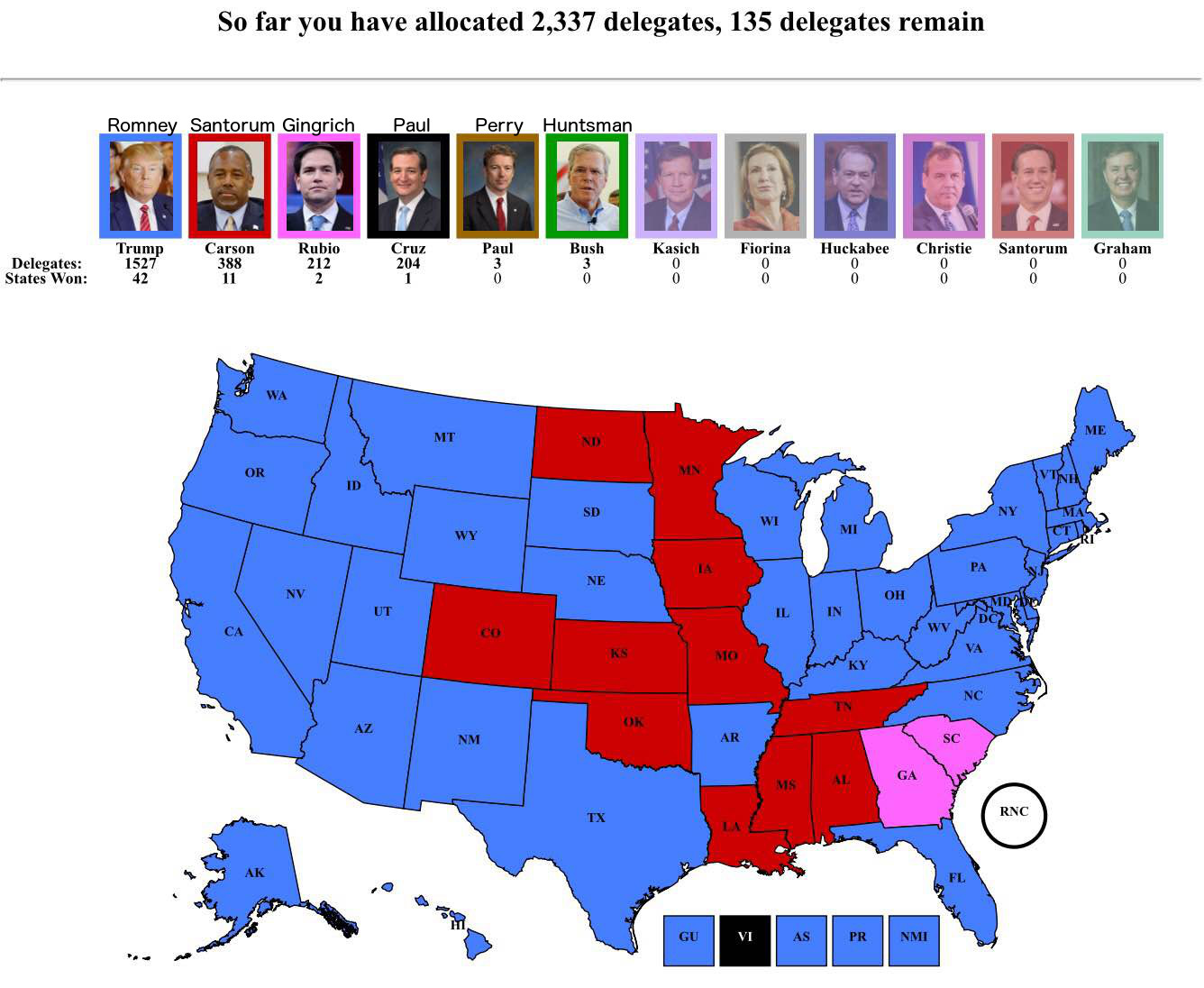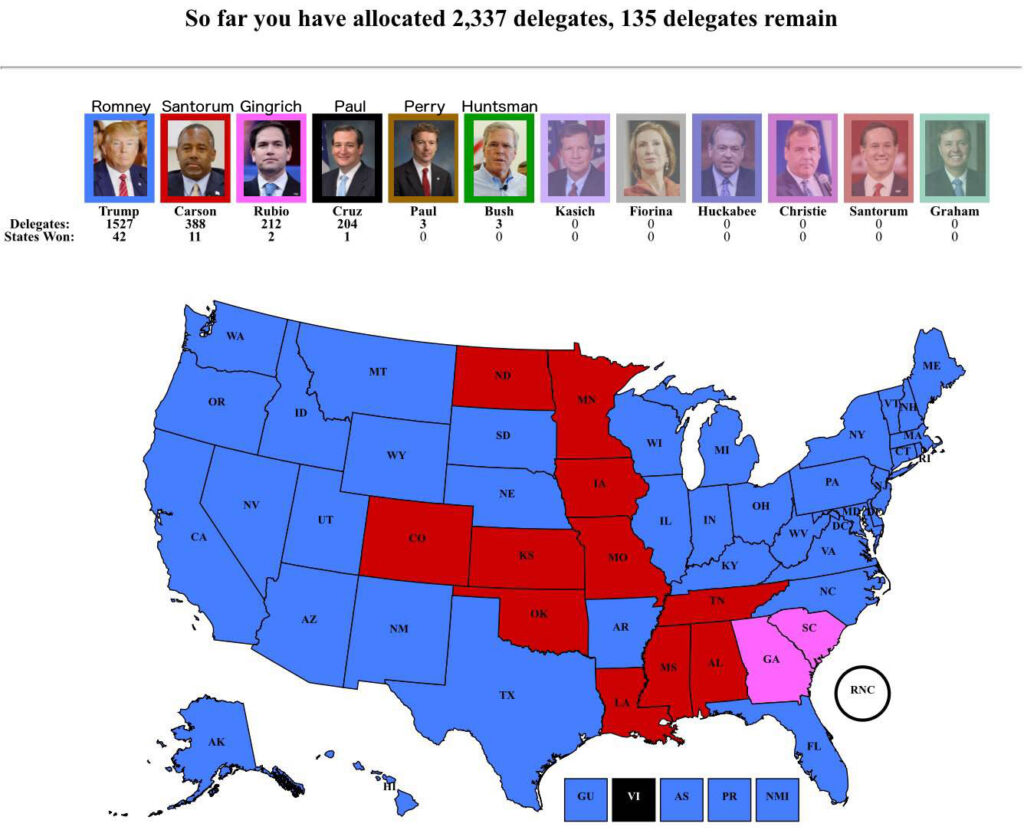
Understanding State Delegates: A State-by-State Breakdown
The American political landscape is complex, with various layers of representation ensuring that citizens’ voices are heard. One crucial aspect of this system is the role of state delegates. These individuals play a significant part in shaping policy and selecting candidates, particularly at the national level. This article provides a comprehensive overview of state delegates by state, explaining their function, selection process, and impact on the political process.
What are State Delegates?
State delegates are individuals chosen to represent their state at a larger assembly, often a national convention. The specific role and responsibilities of these delegates can vary significantly depending on the organization or party they represent. In the context of U.S. politics, they are most commonly associated with the presidential nominating conventions of the Democratic and Republican parties.
At these conventions, state delegates formally cast votes to select their party’s nominee for President and Vice President. They also participate in shaping the party platform, which outlines the party’s stance on key issues. The number of delegates each state receives is typically based on its population, with some variations depending on the party’s rules.
The Delegate Selection Process: A State-by-State Approach
The process of selecting state delegates is not uniform across the country. Each state, and sometimes even each party within a state, has its own rules and procedures. Generally, the selection process falls into one of two main categories: primaries and caucuses.
Primaries
In a primary election, voters cast ballots for their preferred presidential candidate. The results of the primary then determine how the state’s delegates will be allocated. There are two main types of primaries: open and closed.
- Open Primaries: In states with open primaries, any registered voter can participate in either party’s primary, regardless of their own party affiliation.
- Closed Primaries: In states with closed primaries, only registered members of a particular party can vote in that party’s primary.
The way delegates are allocated based on primary results can also vary. Some states use a winner-take-all system, where the candidate who wins the most votes receives all of the state’s delegates. Other states use a proportional system, where delegates are allocated based on the percentage of votes each candidate receives.
Caucuses
Caucuses are meetings of party members at the local level. Participants gather to discuss the candidates and express their support. The results of these caucuses are then used to determine which candidates receive delegates. Caucuses are generally more time-consuming and require a greater level of engagement than primaries.
State-Specific Examples
To illustrate the diversity of delegate selection processes, let’s look at a few examples:
- Iowa: Iowa holds the first caucus in the nation, giving it significant influence in the presidential race. The Iowa caucuses are complex, involving multiple rounds of voting and speeches by supporters of each candidate.
- New Hampshire: New Hampshire holds the first primary in the nation. Like Iowa, New Hampshire’s early primary gives it a significant role in shaping the field of presidential candidates.
- California: California has a large number of delegates, making it a crucial state in the presidential nominating process. California uses a modified closed primary system, where voters who are not registered with a party can still vote in the primary if they register as “No Party Preference.”
- Texas: Texas uses a combination of primaries and caucuses to select its delegates. The primary is open to all registered voters, while the caucuses are open only to registered members of the party.
The Role of State Delegates at the National Convention
Once the state delegates have been selected, they travel to the national convention to formally nominate their party’s presidential and vice-presidential candidates. At the convention, delegates participate in a variety of activities, including:
- Speeches and Rallies: Delegates attend speeches by party leaders and rallies in support of their preferred candidates.
- Committee Meetings: Delegates participate in committee meetings to discuss and shape the party platform.
- Voting: The most important function of state delegates is to cast their votes for the presidential and vice-presidential nominees. The candidate who receives a majority of the delegates’ votes wins the nomination.
The Impact of State Delegates on the Political Process
State delegates play a crucial role in the American political process. They are responsible for selecting the candidates who will represent their party in the general election, and they also help to shape the party’s platform. The selection of state delegates can have a significant impact on the outcome of the presidential race.
For example, if a candidate is able to win a large number of delegates early in the primary season, they may be able to build momentum and secure the nomination. Similarly, if a candidate is able to win the support of influential delegates, they may be able to sway other delegates to vote for them.
The influence of state delegates extends beyond the presidential nominating process. They also play a role in shaping the party’s platform and influencing policy decisions. By participating in committee meetings and advocating for their preferred policies, delegates can help to shape the direction of the party.
Understanding Unbound Delegates
The term “unbound delegate” refers to a state delegate who is not pledged to support a specific candidate at the national convention. In some states, delegates are required to vote for the candidate they were elected to support, at least for the first ballot. However, in other states, delegates are free to vote for whomever they choose, regardless of the results of the primary or caucus.
Unbound delegates can play a significant role in contested nominations, where no candidate has secured a majority of the delegates before the convention. In these situations, unbound delegates can become kingmakers, potentially swinging the nomination to one candidate or another.
The Importance of Local Engagement
Understanding the role of state delegates highlights the importance of local engagement in the political process. By participating in primaries and caucuses, citizens can have a direct impact on the selection of delegates and, ultimately, on the outcome of the presidential election. [See also: How to Participate in Local Politics]
Furthermore, becoming a state delegate is a way to directly influence the political process. Individuals interested in becoming a delegate should contact their local party organization for more information on the selection process in their state.
Conclusion: State Delegates and the Democratic Process
State delegates are a vital component of the American democratic process. They serve as a bridge between the voters and the national party, ensuring that the voices of citizens are heard in the selection of presidential candidates and the shaping of party policy. Understanding the role of state delegates by state empowers citizens to engage more effectively in the political system and to make informed decisions about the future of their country.
The process of selecting state delegates may seem complex, but it is essential for ensuring that the presidential nominating process is fair and representative. By understanding the rules and procedures in their own state, citizens can play a meaningful role in shaping the future of American politics. The impact of well-informed state delegates on the political landscape cannot be overstated. They are the cogs in a machine that, when functioning correctly, accurately reflects the will of the people.